Drug shows Efficacy against Contact Dermatitis
May 15, 2020 by Kamran AhmedThe anti-inflammatory properties of the biologic drug, APOSEC, are already known, as established by various studies in the past. But now researchers from MedUni Vienna have found the biologic wound-healing drug to be effective against contact dermatitis and other similar sensitive skin abrasions.
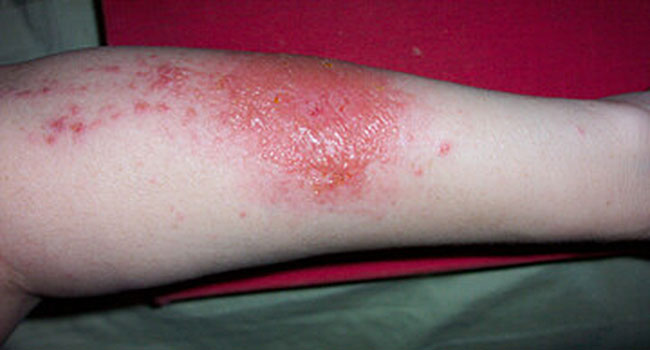
The drug was developed by thoracic surgeon Hendrik Jan Ankersmit from MedUni Vienna. He teamed up with dermatology expert Michael Mildner, also from MedUni Vienna, to investigate the efficacy of APOSEC in the treatment of skin lesions, specifically contact dermatitis.
The findings are favorable, with enough evidence that the drug has the potential to become a more effective alternative to existing skin disease treatments. The active agent is a cell secretome comprising solvent proteins, lipids, and tiny extracellular vesicles emitted by radiation-exposed white blood cells.
The investigators experimented with the topical APOSEC on "a mouse model and ex vivo cultures of human skin" to study its effects on contact dermatitis. The findings showed considerably lower inflammatory reactions. As a result, the allergic response was substantially cut down. The "lipids present in the secretome" made this possible, said the investigators.
"APOSEC comprises natural endogenous substances. We can, therefore, expect it to be particularly well-tolerated," said Mildner.
The researchers examined the effects of the secretome on dendritic cells that are known to be a key element of immune defense. These cells are part of the class of the antigen-presenting cells and are responsible for setting the body's immune system into action when a foreign agent invades the body. But allergies or atopies often disrupt this immune reaction, triggering an undesirable, and unrestrained immune reaction. This triggers skin diseases, resulting in damaged skin.
Pre-clinical studies in the past have already found the secretome to have anti-bacterial properties, besides having revascularization and wound healing effects. More clinical trials are in the pipeline to study the efficacy of APOSEC on other skin diseases, including atopic eczema, psoriasis, and even diabetic foot syndrome.
Learn more at
MEDICAL EXPRESS
About Atopic Dermatitis
Breakthrough Treatment for Eczema and Psoriasis
Sitagliptin plus Phototherapy, A Promising Treatment for Psoriasis
Trial finds Deucravacitinib is Effective For Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis
Investigational Drugs bring hope to those suffering from Psoriasis
Netakimab Clinical Trial reveals its efficacy for treating Psoriasis
Can Eczema Medication given to Children cause Cancer?
Are You Concerned About Eczema? See What Doctors Say!
Combining Two Medications Shows Promising Results in Treating Atopic Dermatitis
Managing Pruritus in Atopic Dermatitis with Ruxolitinib Cream
Is Rocatinlimab Safe and Effective for Treating Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis?
Drug shows Efficacy against Contact Dermatitis
MEDICAL EXPRESS
About Atopic Dermatitis
Breakthrough Treatment for Eczema and Psoriasis
Sitagliptin plus Phototherapy, A Promising Treatment for Psoriasis
Trial finds Deucravacitinib is Effective For Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis
Investigational Drugs bring hope to those suffering from Psoriasis
Netakimab Clinical Trial reveals its efficacy for treating Psoriasis
Can Eczema Medication given to Children cause Cancer?
Are You Concerned About Eczema? See What Doctors Say!
Combining Two Medications Shows Promising Results in Treating Atopic Dermatitis
Managing Pruritus in Atopic Dermatitis with Ruxolitinib Cream
Is Rocatinlimab Safe and Effective for Treating Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis?
Drug shows Efficacy against Contact Dermatitis
Next »
20,000 clinical trials are seeking participants.
Signup and be matched to trials near you
This free service will notify you of current and future clinical trial matches.
Signup and be matched to trials near you
This free service will notify you of current and future clinical trial matches.
