Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor that is commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), has been reported to improve psoriasis. In a clinical trial, researchers investigated whether combining sitagliptin with narrow-band ultraviolet-B (NB-UVB) phototherapy could provide better results for people with moderate psoriasis who do not have T2DM.
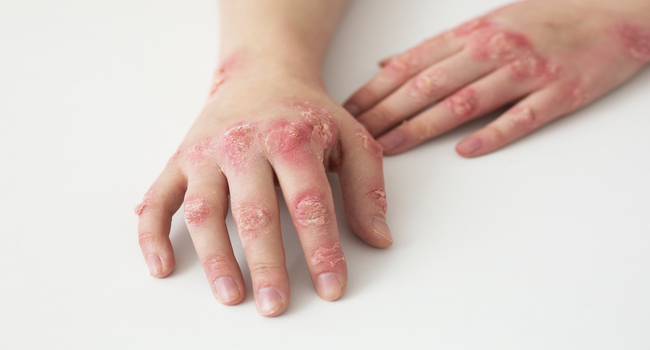
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects approximately 2% of the world's population. It causes skin cells to grow too quickly, resulting in scaly patches and itchiness. While there is no cure for psoriasis, treatments like NB-UVB phototherapy can help alleviate symptoms.
Clinical trial
The trial involved 118 people with moderate psoriasis who were randomly assigned to receive either sitagliptin and NB-UVB phototherapy or NB-UVB phototherapy alone. The primary endpoint was the change in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) from baseline to 24 weeks.
After 24 weeks, the researchers found that the combination therapy group experienced a significantly larger reduction in PASI scores than the NB-UVB phototherapy alone group. The combination therapy group also had significant improvements in quality of life, as measured by the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the EuroQol 5-item questionnaire.
Moreover, the combination therapy group did not experience any serious adverse events related to treatment.
These findings suggest that sitagliptin therapy combined with NB-UVB phototherapy can provide modest improvements in psoriasis severity and quality of life for people with moderate psoriasis who do not have T2DM.
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on a person's physical and emotional well-being. In addition to skin symptoms, people with psoriasis may also experience joint pain and fatigue, which can make it difficult to carry out daily activities. Therefore, finding effective treatments for psoriasis is crucial for improving the lives of those affected by this condition.
NB-UVB phototherapy is a well-established treatment for psoriasis, but combining it with sitagliptin may provide additional benefits. Sitagliptin works by inhibiting DPP-4, an enzyme that breaks down a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). GLP-1 plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels and is also involved in the immune system.
By inhibiting DPP-4, sitagliptin can increase the levels of GLP-1 in the body. This, in turn, may help regulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, which are both key factors in psoriasis.
