Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common respiratory virus that can affect people of all ages, particularly infants and older adults. RSV can lead to mild symptoms like a cold in healthy individuals, but it can cause severe respiratory infections in vulnerable populations, such as premature infants or those with weakened immune systems.
Understanding RSV helps us recognize its symptoms, seek appropriate treatment, and take preventive measures to reduce its spread.
Clinical trials play a vital role in RSV research by testing new treatments, vaccines, and prevention strategies. These trials help scientists and researchers develop more effective ways to manage and prevent RSV infections. By participating in clinical trials, you can contribute to advancing medical knowledge and potentially benefit from innovative treatments or preventive measures.
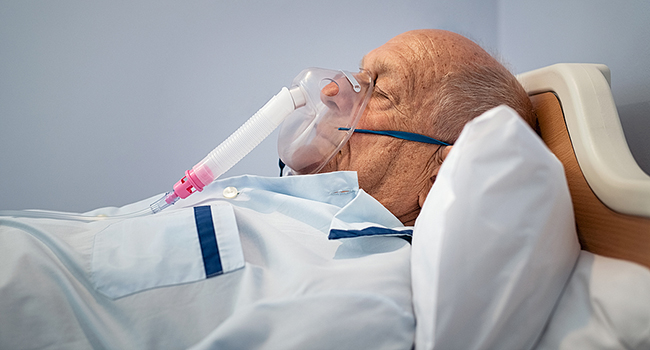
Respiratory Syncytial Virus is a contagious virus that primarily affects the respiratory system. It belongs to the family of viruses called Paramyxoviridae and is a leading cause of respiratory infections worldwide, particularly in infants and young children. RSV can cause a range of respiratory illnesses, from mild cold-like symptoms to severe respiratory distress.
Vaccination against RSV is an active area of research, with ongoing clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of RSV vaccines in preventing infections and reducing disease severity. By promoting RSV awareness and implementing preventive measures, we can minimize the impact of this respiratory virus on public health.
Understanding RSV helps us recognize its symptoms, seek appropriate treatment, and take preventive measures to reduce its spread.
Clinical trials play a vital role in RSV research by testing new treatments, vaccines, and prevention strategies. These trials help scientists and researchers develop more effective ways to manage and prevent RSV infections. By participating in clinical trials, you can contribute to advancing medical knowledge and potentially benefit from innovative treatments or preventive measures.

What is Respiratory Syncytial Virus?
Respiratory Syncytial Virus is a contagious virus that primarily affects the respiratory system. It belongs to the family of viruses called Paramyxoviridae and is a leading cause of respiratory infections worldwide, particularly in infants and young children. RSV can cause a range of respiratory illnesses, from mild cold-like symptoms to severe respiratory distress.
Causes and Transmission of RSV
RSV spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus can also survive on surfaces for several hours, increasing the risk of transmission through contact with contaminated objects. Individuals infected with RSV are most contagious during the first few days of illness but can continue to spread the virus for up to several weeks.Prevention of RSV Infection
Raising awareness about RSV can help prevent its spread and reduce the risk of severe illness, especially in vulnerable populations such as infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Simple preventive measures, such as washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and disinfecting commonly touched surfaces, can help prevent RSV infections.Vaccination against RSV is an active area of research, with ongoing clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of RSV vaccines in preventing infections and reducing disease severity. By promoting RSV awareness and implementing preventive measures, we can minimize the impact of this respiratory virus on public health.
Symptoms of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection
Common Symptoms of RSV Infection
The symptoms of RSV infection can vary depending on the age and overall health of the individual. Common symptoms include:- Runny or stuffy nose
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Fever
- Wheezing
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid breathing
- Loss of appetite
- Irritability, especially in infants and young children
In severe cases, RSV infection can lead to complications such as bronchiolitis or pneumonia, which may require medical intervention.
Differences in Symptoms between Children and Adults
Infants and young children are more susceptible to severe RSV infections compared to healthy adults. In infants, symptoms of RSV infection may include:- Difficulty breathing
- Wheezing or gasping for breath
- Cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin or lips due to lack of oxygen)
- Poor feeding or reduced appetite
- Lethargy or decreased activity
In older children and adults, RSV symptoms are typically milder and may resemble those of a common cold. However, individuals with underlying health conditions or weakened immune systems may experience more severe symptoms and are at increased risk of complications from RSV infection.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of RSV infection, especially in infants and young children, enables one to seek prompt medical attention to prevent complications. Early detection and appropriate management can help reduce the severity of RSV illness and improve outcomes for affected individuals.
While most cases of Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection resolve without long-term consequences, severe infections can lead to complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Currently, there is no specific antiviral medication available to treat Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection. Treatment for RSV typically focuses on managing symptoms and providing supportive care to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. Common treatment options may include:
Before starting any medication or treatment for RSV, discuss the potential risks and benefits with a doctor. They can guide the safest and most effective treatment options based on individual needs and medical history.
Clinical trials are research studies that evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new medical treatments, interventions, or preventive measures. These trials are key in advancing medical knowledge, improving patient care, and developing innovative therapies for various diseases and conditions, including Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection.
The significance of clinical trials lies in their ability to generate scientific evidence about the safety and efficacy of new treatments or interventions. By systematically testing experimental therapies in controlled settings, clinical trials provide valuable insights into their potential benefits and risks, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions about patient care.
Clinical trials typically follow a structured protocol to ensure participant safety and the integrity of study results. Participants in clinical trials may receive investigational treatments, standard-of-care therapies, or placebos, depending on the study design. Throughout the trial, researchers collect data on participant outcomes to assess the effectiveness and safety of the intervention under investigation.
CenTrial uses advanced algorithms and personalized matching technology to notify participants about RSV clinical trials based on their health profiles, preferences, and eligibility. CenTrial can efficiently identify suitable study opportunities for individuals interested in contributing to RSV research.
Through its user-friendly interface, CenTrial enables people to explore research opportunities, learn about potential study options, and connect with researchers conducting RSV-related studies. By bridging the gap between researchers and participants, CenTrial facilitates collaboration and innovation in RSV research, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes and public health.
RSV is a contagious virus that primarily affects the respiratory system, causing a range of symptoms from mild cold-like symptoms to severe respiratory distress. While there is no specific antiviral medication available to treat RSV, supportive care measures can help alleviate symptoms and promote recovery. Clinical trials have recently developed vaccines that can protect the young and the aged to combat this respiratory infection.
Raising awareness about RSV helps to prevent its spread and reduce the burden of respiratory illness, particularly in vulnerable populations such as infants and older adults.
People affected by RSV or interested in contributing to scientific progress can explore clinical trial opportunities through CenTrial.org. CenTrial is a valuable resource for informing individuals about clinical trials that match their profile and providing access to cutting-edge treatments and research opportunities.
By understanding the symptoms of RSV, seeking timely medical care, and considering participation in clinical trials, individuals can play an active role in managing their health and contributing to the advancement of medical science.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of RSV infection, especially in infants and young children, enables one to seek prompt medical attention to prevent complications. Early detection and appropriate management can help reduce the severity of RSV illness and improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Long-term Effects and Complications of RSV
While most cases of Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection resolve without long-term consequences, severe infections can lead to complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Persistent Respiratory Symptoms: Some people may experience persistent respiratory symptoms following RSV infection, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. These symptoms may persist for weeks or even months after the initial infection has cleared.It's essential for those who have experienced severe RSV infection to monitor their respiratory health closely and seek medical attention if they develop any concerning symptoms or complications. By understanding the potential long-term effects of RSV, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and prevent future respiratory problems.
Recurrent Respiratory Infections: RSV infection can weaken the immune system and make people more susceptible to recurrent respiratory infections, including colds, flu, and pneumonia. This increased susceptibility to infections can lead to frequent illness and may require ongoing medical management.
Asthma Exacerbations: RSV infection has been linked to the development and exacerbation of asthma in children and adults. Individuals with a history of RSV infection may experience more frequent asthma attacks or worsening of asthma symptoms following respiratory illnesses.
Chronic Lung Disease: In severe cases, RSV infection can cause damage to the lungs, leading to chronic lung disease. Chronic lung conditions, such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, may result in long-term respiratory impairment and reduced lung function.
Respiratory Failure: Severe RSV infection can progress to respiratory failure, a life-threatening condition where the lungs are unable to provide adequate oxygen to the body. Respiratory failure may require intensive medical intervention, including mechanical ventilation, to support breathing and oxygenation.
Treatment of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection
Currently, there is no specific antiviral medication available to treat Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection. Treatment for RSV typically focuses on managing symptoms and providing supportive care to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. Common treatment options may include:- Symptomatic Relief: Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be used to reduce fever and relieve pain associated with RSV infection. Additionally, saline nasal drops or sprays can help alleviate nasal congestion and improve breathing.
- Oxygen Therapy: In severe cases of RSV infection, particularly in infants or individuals with respiratory distress, supplemental oxygen may be administered to ensure adequate oxygenation of the body.
- Fluid Replacement: It's essential to maintain hydration, especially in infants and young children who may have difficulty feeding or drinking due to respiratory symptoms. Oral rehydration solutions or intravenous fluids may be necessary to prevent dehydration.
- Hospitalization: Some individuals, particularly infants or those with underlying health conditions, may require hospitalization for close monitoring and intensive care management. Hospitalization may be necessary to provide respiratory support, such as mechanical ventilation, in severe cases of RSV infection.
Role of Supportive Care in Managing RSV Symptoms
Supportive care plays a vital role in managing the symptoms of Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection and promoting recovery. While there is no specific antiviral medication available to treat RSV, supportive care focuses on relieving symptoms and providing comfort to individuals affected by the virus:- Rest: Adequate rest is important for people with RSV infection to allow their bodies to recover and fight off the virus effectively. Encouraging rest and minimizing physical exertion can help conserve energy and promote healing.
- Hydration: Maintaining hydration is vital, especially for infants and young children who may experience difficulty feeding or drinking due to respiratory symptoms. Offering fluids regularly, such as breast milk, formula, water, or oral rehydration solutions, can prevent dehydration and support recovery.
- Humidified Air: Using a humidifier or steam inhalation can help moisten the air and alleviate respiratory symptoms such as nasal congestion and coughing. Breathing in humidified air can soothe irritated airways and make breathing more comfortable for individuals with RSV infection.
- Nasal Suctioning: Nasal congestion is a common symptom of RSV infection, particularly in infants and young children. Using a bulb syringe or nasal aspirator to remove excess mucus from the nasal passages can improve breathing and reduce discomfort.
- Elevating the Head: Elevating the head of the bed or using pillows to prop up the upper body can help ease breathing difficulties associated with RSV infection, especially during sleep.
Side Effects of RSV Medications and Treatments
While supportive care is generally well-tolerated and considered safe for managing RSV symptoms, some medications and treatments may have potential side effects or risks. It's important to be aware of these potential side effects and discuss them with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment for RSV. Some common side effects of RSV medications and treatments are:- Gastrointestinal Upset: Certain medications used to treat RSV symptoms, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may cause gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea in some individuals.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to medications or treatments used to manage RSV symptoms. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Seek medical attention immediately if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction.
- Respiratory Complications: In rare cases, certain medications or treatments used to manage RSV symptoms may exacerbate respiratory problems or lead to respiratory complications, especially in individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions such as asthma or COPD.
- Drug Interactions: It's essential to be aware of potential drug interactions when using multiple medications to manage RSV symptoms. Certain medications may interact with each other, leading to adverse effects or reduced effectiveness of treatment.
Before starting any medication or treatment for RSV, discuss the potential risks and benefits with a doctor. They can guide the safest and most effective treatment options based on individual needs and medical history.
Clinical Trials for Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Clinical trials are research studies that evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new medical treatments, interventions, or preventive measures. These trials are key in advancing medical knowledge, improving patient care, and developing innovative therapies for various diseases and conditions, including Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection.The significance of clinical trials lies in their ability to generate scientific evidence about the safety and efficacy of new treatments or interventions. By systematically testing experimental therapies in controlled settings, clinical trials provide valuable insights into their potential benefits and risks, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions about patient care.
Clinical trials typically follow a structured protocol to ensure participant safety and the integrity of study results. Participants in clinical trials may receive investigational treatments, standard-of-care therapies, or placebos, depending on the study design. Throughout the trial, researchers collect data on participant outcomes to assess the effectiveness and safety of the intervention under investigation.
CenTrial's Role in Matching Participants to RSV Clinical Trials
CenTrial.org is dedicated to connecting people to clinical trials relevant to their health conditions or medical needs. CenTrial is a valuable resource for those seeking opportunities to participate in research studies, including ones focused on Respiratory Syncytial Virus.CenTrial uses advanced algorithms and personalized matching technology to notify participants about RSV clinical trials based on their health profiles, preferences, and eligibility. CenTrial can efficiently identify suitable study opportunities for individuals interested in contributing to RSV research.
Through its user-friendly interface, CenTrial enables people to explore research opportunities, learn about potential study options, and connect with researchers conducting RSV-related studies. By bridging the gap between researchers and participants, CenTrial facilitates collaboration and innovation in RSV research, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes and public health.
Frequently Asked Questions about RSV
How long does RSV infection last?
The duration of RSV infection varies depending on individual factors and the severity of symptoms. In most cases, RSV symptoms typically resolve within one to two weeks.Is RSV serious?
While RSV infection is often mild and self-limiting in healthy individuals, it can lead to severe respiratory illness, particularly in vulnerable populations such as infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems.Can RSV turn into pneumonia?
In severe cases, RSV infection can lead to complications such as pneumonia, especially in vulnerable populations or individuals with underlying health conditions.Is there a vaccine for RSV?
There are vaccines available such as Beyfortus for children, as well as two vaccines, Arexvy and Abrysvo, for people aged 60 and over that were approved by the FDA in May 2023.
Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to evaluate RSV vaccines that aim to prevent infections and reduce disease severity.Can RSV go away on its own?
In many cases, RSV infection resolves on its own without specific treatment. Supportive care measures, such as rest, hydration, and symptom management, can help alleviate discomfort and promote recovery.Can RSV be treated with antibiotics?
RSV is a viral infection, and antibiotics are not effective against viruses. Treatment for RSV typically focuses on relieving symptoms and providing supportive care to manage respiratory symptoms and prevent complications.
In Summary
RSV is a contagious virus that primarily affects the respiratory system, causing a range of symptoms from mild cold-like symptoms to severe respiratory distress. While there is no specific antiviral medication available to treat RSV, supportive care measures can help alleviate symptoms and promote recovery. Clinical trials have recently developed vaccines that can protect the young and the aged to combat this respiratory infection.Raising awareness about RSV helps to prevent its spread and reduce the burden of respiratory illness, particularly in vulnerable populations such as infants and older adults.
People affected by RSV or interested in contributing to scientific progress can explore clinical trial opportunities through CenTrial.org. CenTrial is a valuable resource for informing individuals about clinical trials that match their profile and providing access to cutting-edge treatments and research opportunities.
By understanding the symptoms of RSV, seeking timely medical care, and considering participation in clinical trials, individuals can play an active role in managing their health and contributing to the advancement of medical science.
