Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. This buildup of fat can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver cells over time. While a small amount of fat in the liver is normal, excessive accumulation can result in health complications.
Understanding and managing fatty liver disease is imperative due to its potential impact on overall health and well-being. Left untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to more severe conditions, such as liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. By taking proactive steps to manage the condition, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their quality of life.
Clinical trials play a vital role in advancing our understanding and treatment of fatty liver disease. These research studies allow scientists and medical professionals to test new medications, therapies, and interventions aimed at preventing, diagnosing, and treating the disease. By participating in clinical trials, individuals with fatty liver disease can contribute to developing new treatments and potentially benefit from cutting-edge therapies.
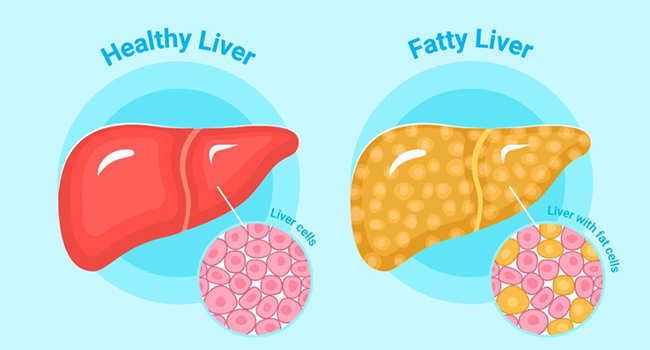
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common form of fatty liver disease and is not related to excessive alcohol consumption. It encompasses a range of conditions, from simple fatty liver to more severe forms, such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and liver cell damage.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):
Alcoholic fatty liver disease develops as a result of chronic alcohol consumption. It is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells due to the toxic effects of alcohol. Without intervention, alcoholic fatty liver disease can progress to more severe liver damage, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Understanding and managing fatty liver disease is imperative due to its potential impact on overall health and well-being. Left untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to more severe conditions, such as liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. By taking proactive steps to manage the condition, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their quality of life.
Clinical trials play a vital role in advancing our understanding and treatment of fatty liver disease. These research studies allow scientists and medical professionals to test new medications, therapies, and interventions aimed at preventing, diagnosing, and treating the disease. By participating in clinical trials, individuals with fatty liver disease can contribute to developing new treatments and potentially benefit from cutting-edge therapies.

What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. This excess fat can impair the liver's ability to function properly and may lead to inflammation and damage over time.Types of Fatty Liver Disease
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common form of fatty liver disease and is not related to excessive alcohol consumption. It encompasses a range of conditions, from simple fatty liver to more severe forms, such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and liver cell damage.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):
Alcoholic fatty liver disease develops as a result of chronic alcohol consumption. It is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells due to the toxic effects of alcohol. Without intervention, alcoholic fatty liver disease can progress to more severe liver damage, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Causes and Risk Factors of Fatty Liver
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of fatty liver disease:- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, increases the risk of fatty liver disease.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in refined sugars, saturated fats, and processed foods can contribute to fat accumulation in the liver.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity can increase the risk of fatty liver disease.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can predispose individuals to fatty liver disease, including:- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels are associated with an increased risk of fatty liver disease.
- Metabolic Syndrome: A cluster of conditions, including obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance, can contribute to fatty liver disease.
Medications
Some medications may contribute to the development or worsening of fatty liver disease:- Corticosteroids
- Antiviral medications
- Methotrexate
Signs and Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Symptoms of fatty liver disease may vary depending on the severity of the condition but can include:- Fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort, or pain
- Elevated liver enzymes
- In some cases, individuals with fatty liver disease may develop a skin rash characterized by itching, redness, and rash on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
Medical History and Physical Examination
Diagnosing fatty liver disease typically begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. During the medical history, the healthcare provider will inquire about the patient's symptoms, lifestyle habits, medical conditions, and any medications they may be taking. A physical examination may reveal signs of liver enlargement or tenderness.Diagnostic Tests
Following the medical history and physical examination, healthcare providers may order diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis of fatty liver disease, such as:- Blood Tests: Blood tests can assess liver function and detect elevated liver enzymes, which may indicate liver inflammation or damage.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can provide detailed images of the liver and help identify fatty infiltration.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be performed to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination. This procedure can confirm the presence of fatty liver disease and assess the degree of liver damage. However, it is usually reserved for cases where the diagnosis is uncertain or when additional information is needed to guide treatment decisions.
Treatment of Fatty Liver Disease
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
Fatty Liver Disease Diet:A healthy diet plays a crucial role in managing fatty liver disease. Some dietary recommendations for individuals with fatty liver disease are:
- Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limiting intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugars.
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, as it can worsen liver damage.
- Monitoring portion sizes and practicing mindful eating habits.
- Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines to promote weight loss and improve liver health.
Fatty Liver Disease Self-Care Tips:
In addition to dietary changes, people with fatty liver disease can take self-care steps to improve their overall health and well-being:
In addition to dietary changes, people with fatty liver disease can take self-care steps to improve their overall health and well-being:
- Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels and managing conditions such as diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
- Avoiding smoking and minimizing exposure to environmental toxins.
- Getting regular exercise to promote liver health and overall wellness.
- Following recommendations from healthcare providers regarding medication use and lifestyle modifications.
Medical Treatment
Medications for Fatty Liver Disease:While there is no specific medication approved for the treatment of fatty liver disease, doctors may prescribe certain medications to manage underlying conditions or symptoms such as:
- Insulin-sensitizing agents for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes.
- Lipid-lowering medications to manage high cholesterol levels.
- Vitamin E supplements in some cases of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) to reduce liver inflammation.
Medications to Avoid with Fatty Liver Disease:
People with fatty liver disease should be cautious about certain medications that can worsen liver damage. These may include:
People with fatty liver disease should be cautious about certain medications that can worsen liver damage. These may include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen in high doses.
- Some prescription medications, such as certain antibiotics, antivirals, and immunosuppressants.
- Herbal supplements and alternative remedies, as their safety and efficacy in liver disease, are not well established.
Clinical Trials for Fatty Liver Disease
Clinical trials are essential for advancing our understanding and treatment of fatty liver disease. These research studies allow scientists and medical professionals to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new medications, therapies, and interventions for managing the condition. By participating in clinical trials, individuals with fatty liver disease can contribute to developing innovative treatments and potentially benefit from access to cutting-edge therapies that may not be available otherwise.
Role of CenTrial.org in Connecting Patients with Clinical Trials
CenTrial.org plays a vital role in connecting patients with fatty liver disease to clinical trials that may be relevant to their condition. As a centralized platform, CenTrial matches patients and healthy volunteers to ongoing clinical trials, allowing you to explore potential treatment options and participate in research studies that meet your needs and preferences. By facilitating connections between patients and researchers, CenTrial helps accelerate the pace of scientific discovery and the development of new treatments for fatty liver disease.
In Summary
Fatty liver disease is a prevalent condition that can have significant implications for an individual's health and well-being. Fatty liver disease affects about 25% of the world's population. Understanding the risk factors, signs, and management strategies is essential for effectively addressing this condition and reducing the risk of complications.If you or someone you know is affected by fatty liver disease, it is important to seek information and support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and reputable online resources. By staying informed and proactive, you can take control of your health and make informed decisions about your care. Remember that you are not alone, and there are resources available to help you navigate this journey.
CenTrial.org provides opportunities for people with fatty liver disease to receive notifications of clinical trials that may offer new treatment options and advancements in research. Through its centralized platform, CenTrial facilitates access to ongoing trials, allowing patients to explore potential opportunities for participation.
__________
About Liver Disease
