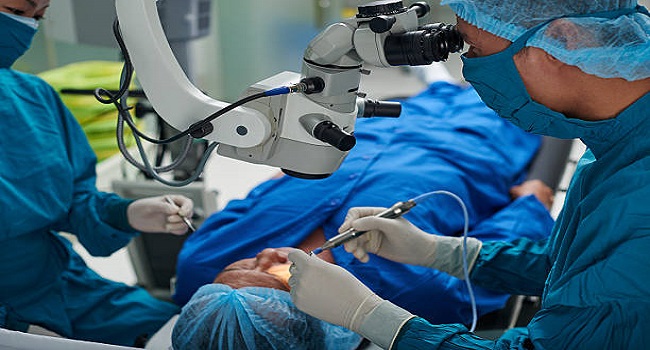
A clinical trial explored the efficacy of Schlemm canal microstents, also called Hydrus microstent, together with Phacoemulsification in Open-Angle Glaucoma.
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in old people worldwide. It is a condition that can cause irreversible vision loss and blindness if left untreated. It's a disease that affects the optic nerve, which is the nerve that sends visual information from the eye to the brain. It is characterized by a build-up of fluid in the front part of the eye resulting in increased pressure in the eye. There are different types of glaucoma, but the most common form is called open-angle glaucoma. It progresses gradually, where the eye does not drain fluid as well as it should (like a clogged drain). As a result, eye pressure builds and starts to damage the optic nerve.
Fortunately, there are treatments available for glaucoma, including medications and surgery. One surgical treatment that has been gaining attention in recent years is the Schlemm canal micro stent, also known as the Hydrus microstent. This is a tiny device that is implanted in the eye to help improve the flow of fluid out of the eye, which can reduce intraocular pressure and prevent further damage to the optic nerve. However, long-term clinical data on its efficacy has been deficient.
Clinical Trial
A group of researchers conducted a clinical trial to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the Hydrus microstent in combination with cataract surgery for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma. The trial followed patients for three years after the procedure to assess the long-term outcomes.It included 106 patients with open-angle glaucoma who underwent cataract surgery along with the Hydrus microstent implantation. The researchers evaluated various factors, including intraocular pressure, increased medication use, glaucoma re-operation, and laser surgery at multiple time points over the three-year period.
