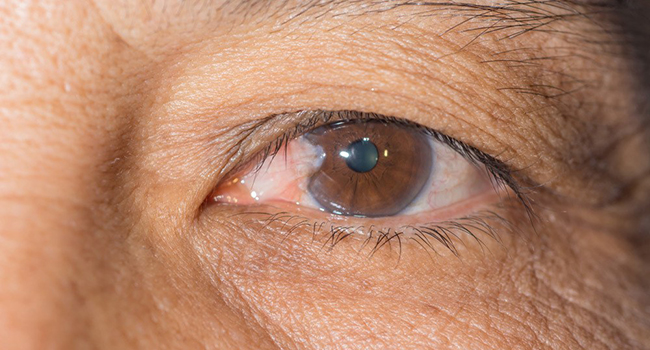
Pterygium is a common eye disorder that occurs when a growth of tissue develops on the conjunctiva, which is the clear tissue that covers the white part of the eye. Pterygium can cause redness, irritation, and sometimes vision problems. Surgical removal of the pterygium is often necessary, and conjunctival autologous graft (CAG) is a technique that has been used for many years to repair the area where the pterygium was removed. In this clinical trial, researchers compared two methods of graft attachment: autologous fibrin glue and traditional sutures.
Autologous fibrin glue is a substance that can be prepared from the patient's own blood components. The glue is created by collecting plasma from the patient and enhancing it with calcium gluconate. The resulting mixture can then be used to attach the graft. The traditional method of attachment is through the use of sutures.
Clinical Trial
The study enrolled 61 patients who underwent pterygium surgery with CAG. The patients were randomly assigned to receive either autologous fibrin glue or traditional sutures. The surgical time and postoperative assessments were evaluated on Days 1, 7, 21, 30, and 180. The study measured postoperative edema and pain and assessed the recurrence of the pterygium 6 months after surgery.
Results
The results of the study showed that both techniques were successful in graft adherence, with 83.60% of patients maintaining graft presence at the end of follow-up. However, the autologous fibrin glue had a higher graft loss rate, with 10 patients (10/33) losing their graft in the glue group. Furthermore, only 69.70% of patients in the glue group maintained graft presence in the fourth week, compared to 100% of patients in the suture group. The difference was statistically significant.
