Hepatitis C is a blood-borne contagious disease of the liver caused by the Hepatitis- C virus. It may lead to severe disease of the liver and even liver cancers.
It is mostly seen in people who inject recreational drugs through unsterilized needles.
Transmission of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is usually a blood-borne disease that may spread via:- Reuse and sharing of unsterilized needles especially by intravenous drug abusers
- Sharing razor and toothbrush of a person infected with hepatitis C
- Vertical transmission from a pregnant mother to her unborn baby
- Unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person, particularly male to male intercourse with an infected person (rare)
It however does not spread from kissing, hugging, or sharing foods with an infected person. It also does not spread through breast milk.
Signs and Symptoms of Hepatitis C
Four-fifth of the people infected with the virus remains asymptomatic. However, for the people who do develop symptoms of the disease, they do so after 2 weeks to 6 months. These patients present with:- Passage of a pale, clay-colored stool
- Dark urine
- Increased body temperature
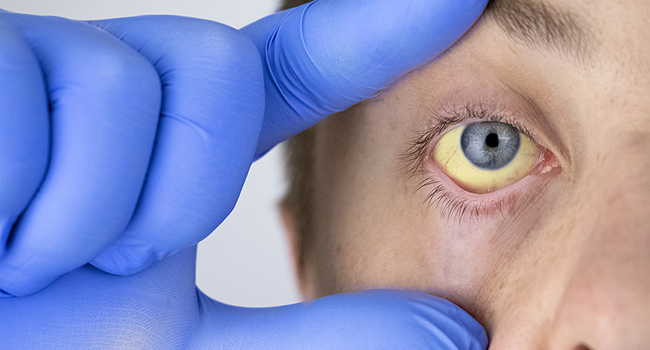
- Yellowish discoloration of the skin and the sclera (white part of your eyes)
- Joint pain
- Abdominal discomfort
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tiredness and general body weakness
These symptoms after appearing may persist for 2 to 12 weeks.
Diagnosis of Hepatitis C
For the diagnosis of Hepatitis-C your doctor will order you two tests:- Antibody Test: This test involves detecting the presence of Anti-HBC Antibodies in the blood. Antibodies are produced in the body in response to the infection to fend it off. A positive antibody test signifies that you have been infected with the virus at some stage; however, a negative test does not always rule out infection as it may take some time for your body to develop these antibodies against the virus.
- PCR: PCR test is indicated in cases with positive antibody test to detect if the virus is still present in the body and multiply. It does so by measuring the viral nucleic acid in the blood. A positive result for the PCR test signifies the presence of active Hepatitis-C infection.
Other tests indicated to detect liver damage include
- Liver function test: It helps to assess the levels of liver enzymes that indicate liver damage.
- Magnetic resonance electrography (MRE): It helps in detecting Hepatitis-C induced scarring of the liver using the MRI technique.
- Liver biopsy: The test involves taking out a small sample of liver tissue and sending it for investigations to check for liver damage. It is an invasive method of diagnosing liver disease.
Management of Hepatitis C
Most cases of HCV remain asymptomatic and your body clears out most of the infection, thus medical management of the condition is not always required. It is needed in cases where your body is unable to fend off the infection and the disease has gone to chronicity.- Antiviral drugs: These drugs are used to remove viral pathogens from the bloodstream. These drugs are effective in treating more than 95% of patients with HCV infection. These drugs do not however provide immunity from the disease, so the risk factors should be avoided even after treatment. Newly developed antivirals like Simeprevir, Sofosbuvir, and Daclatasvir have shorter treatment courses and have been shown to make the treatment even more effective.
- Liver transplant: It is indicated in patients in whom hepatitis C has led to irreversible liver damage. It involves removing the infected liver and transferring healthy liver from a donor. Antiviral medications are still required after liver transplant to prevent infection of the transplanted liver.
