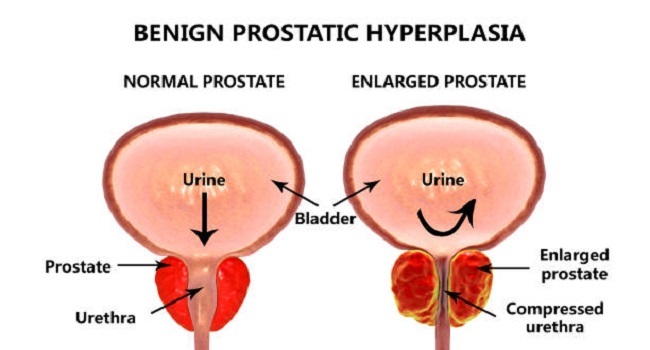
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), one of the most common diseases affecting men as they age, often causes lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) that can negatively affect daily activities and quality of life (QoL). There are many treatments available for BPH, some of which may cause sexual dysfunction.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, is the most common benign tumor found in men. It can cause a variety of symptoms such as LUTS, urinary retention, hematuria, and recurrent urinary tract infections. Treatments for BPH include pharmacotherapy and the current gold standard of transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
However, both are associated with a significant risk to sexual function. Since sexual health is a highly important aspect of QoL, newer techniques are being discovered aimed at preserving sexual function in BPH patients. One such option is a temporarily implanted nitinol device. It is a mechanical device that re-models the bladder neck and prostatic urethra by self-expansion.
Clinical Trial
A clinical trial evaluated the effectiveness of a temporarily implanted Nitinol device in treating LUTS and its impact on sexual function.The trial, published in the Journal of Endourology, involved 185 men with BPH who were treated either with a Nitinol device or a similar non-effective procedure. The device was inserted into the prostate through the urethra and temporarily expanded to relieve pressure on the urethra and improve urine flow.
